CCU Hub:
Transforming CO2 to Create a Sustainable Future
CCU Hub:
Transforming CO2 to Create a Sustainable Future
CCU Hub:
Transforming CO2 to Create a Sustainable Future
Refractories:
RHI Magnesita is the leading global supplier of high-grade refractory products and solutions for high-temperature processes over 1,200°C in industries such as steel, cement, non-ferrous metals, and glass. With a fully integrated value chain, the company delivers raw materials, products, and performance-based services.
Refractories are essential for protecting people and equipment from extreme heat and chemical exposure and play a vital role in metal recycling and other circular economy processes.




1 tonne of STEEL
demands ~10-15 kg of refractories
1 tonne of CEMENT
demands ~1 kg of refractories
1 tonne of GLASS
demands ~4 kg of refractories
1 tonne of ALUMINIUM
demands ~6 kg of refractories
1 tonne of COPPER
demands ~3 kg of refractories
the building blocks of modern life
Refractories:
RHI Magnesita is the leading global supplier of high-grade refractory products and solutions for high-temperature processes over 1,200°C in industries such as steel, cement, non-ferrous metals, and glass. With a fully integrated value chain, the company delivers raw materials, products, and performance-based services.
Refractories are essential for protecting people and equipment from extreme heat and chemical exposure and play a vital role in metal recycling and other circular economy processes.

1 tonne of STEEL
demands ~10-15 kg of refractories

1 tonne of CEMENT
demands ~1 kg of refractories

1 tonne of GLASS
demands ~4 kg of refractories

1 tonne of ALUMINIUM
demands ~6 kg of refractories

1 tonne of COPPER
demands ~3 kg of refractories
the building blocks of modern life
Refractories:
RHI Magnesita is the leading global supplier of high-grade refractory products and solutions for high-temperature processes over 1,200°C in industries such as steel, cement, non-ferrous metals, and glass. With a fully integrated value chain, the company delivers raw materials, products, and performance-based services.
Refractories are essential for protecting people and equipment from extreme heat and chemical exposure and play a vital role in metal recycling and other circular economy processes.

1 tonne of STEEL
demands ~10-15 kg of refractories

1 tonne of CEMENT
demands ~1 kg of refractories

1 tonne of GLASS
demands ~4 kg of refractories

1 tonne of ALUMINIUM
demands ~6 kg of refractories

1 tonne of COPPER
demands ~3 kg of refractories
the building blocks of modern life
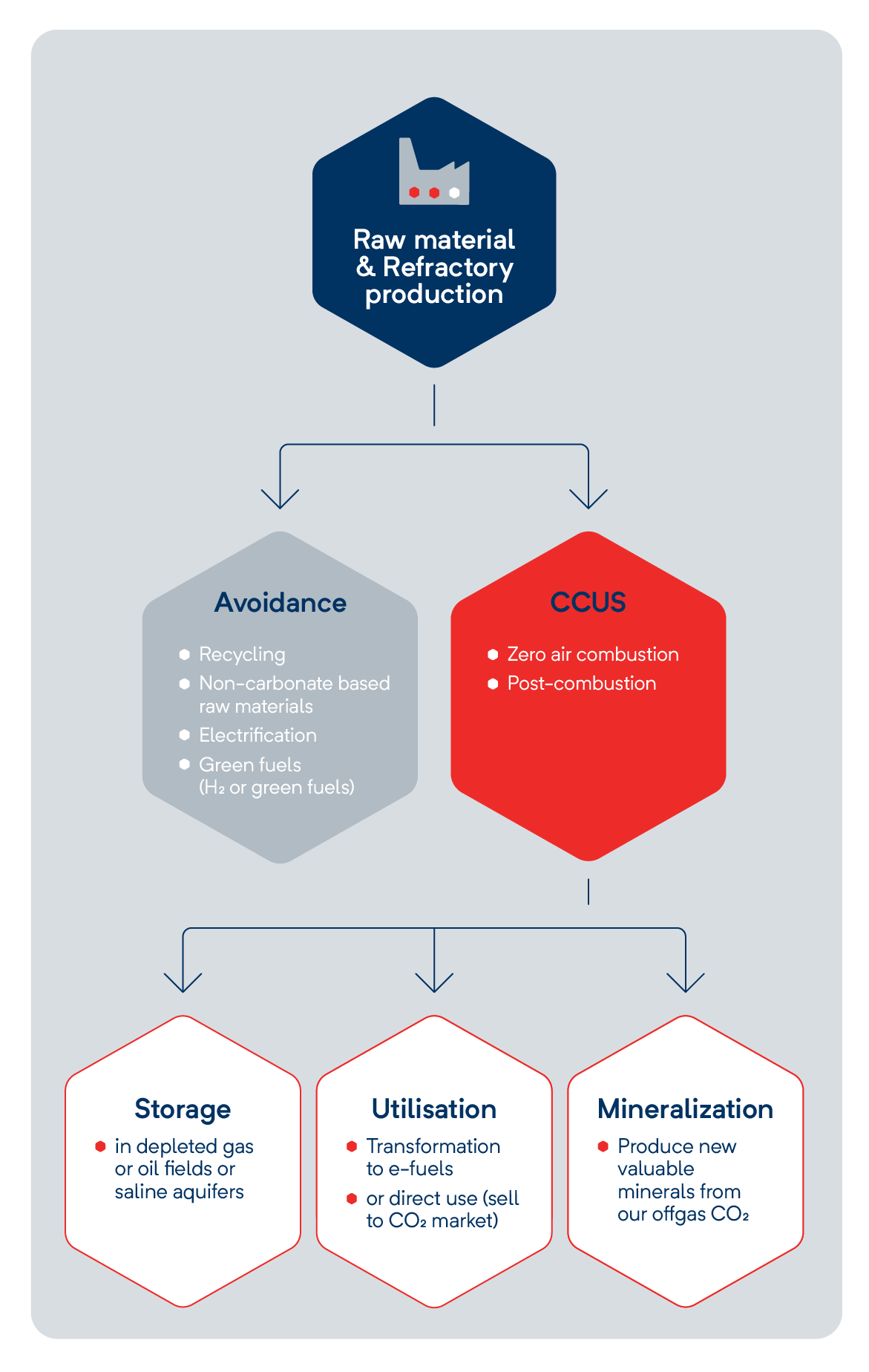
Refractory production is a hard to abate, energy intensive process with a high CO2 intensity. While switching to green fuels and recycling help reduce avoidable emissions, only Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU) can address unavoidable process emissions. For instance, RHI Magnesita is collaborating with the Australian Green Tech Start-Up MCi Carbon to develop an innovative CCU mineralization technology that has the potential to eliminate process emissions.
Decarbonization Roadmap
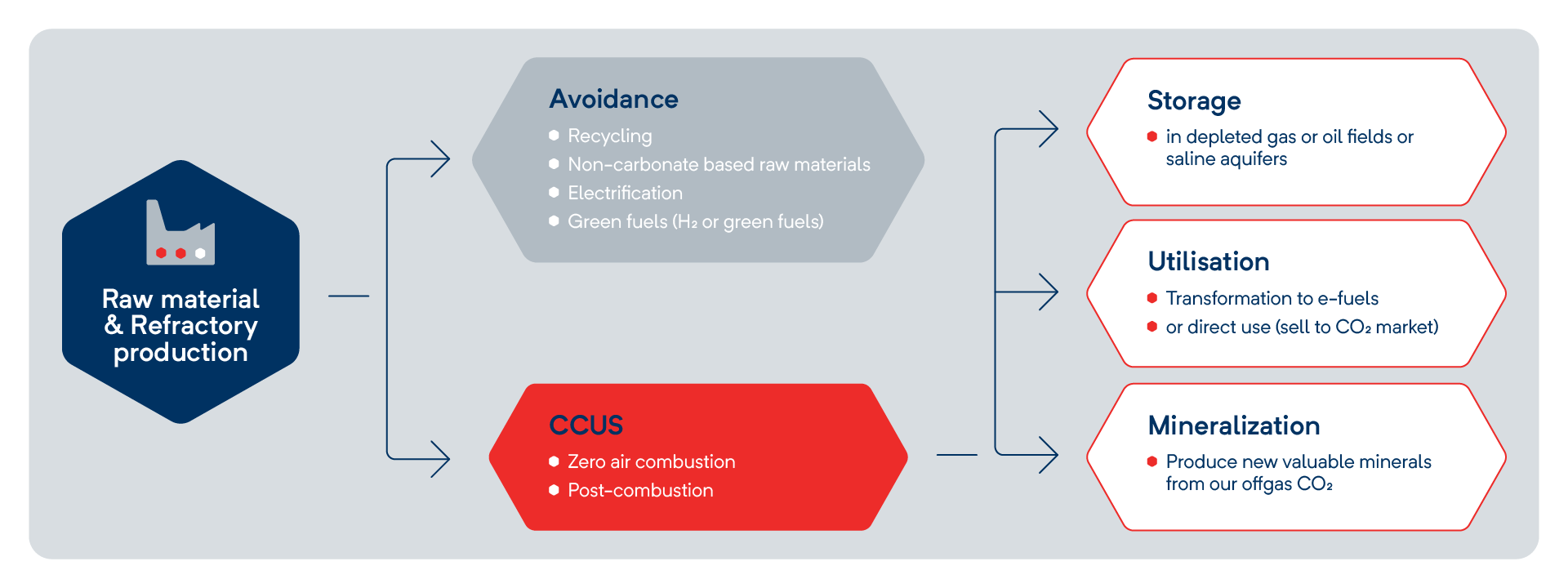
Refractory production is a hard to abate, energy intensive process with a high CO2 intensity. While switching to green fuels and recycling help reduce avoidable emissions, only Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU) can address unavoidable process emissions. For instance, RHI Magnesita is collaborating with the Australian Green Tech Start-Up MCi Carbon to develop an innovative CCU mineralization technology that has the potential to eliminate process emissions.
Decarbonization Roadmap
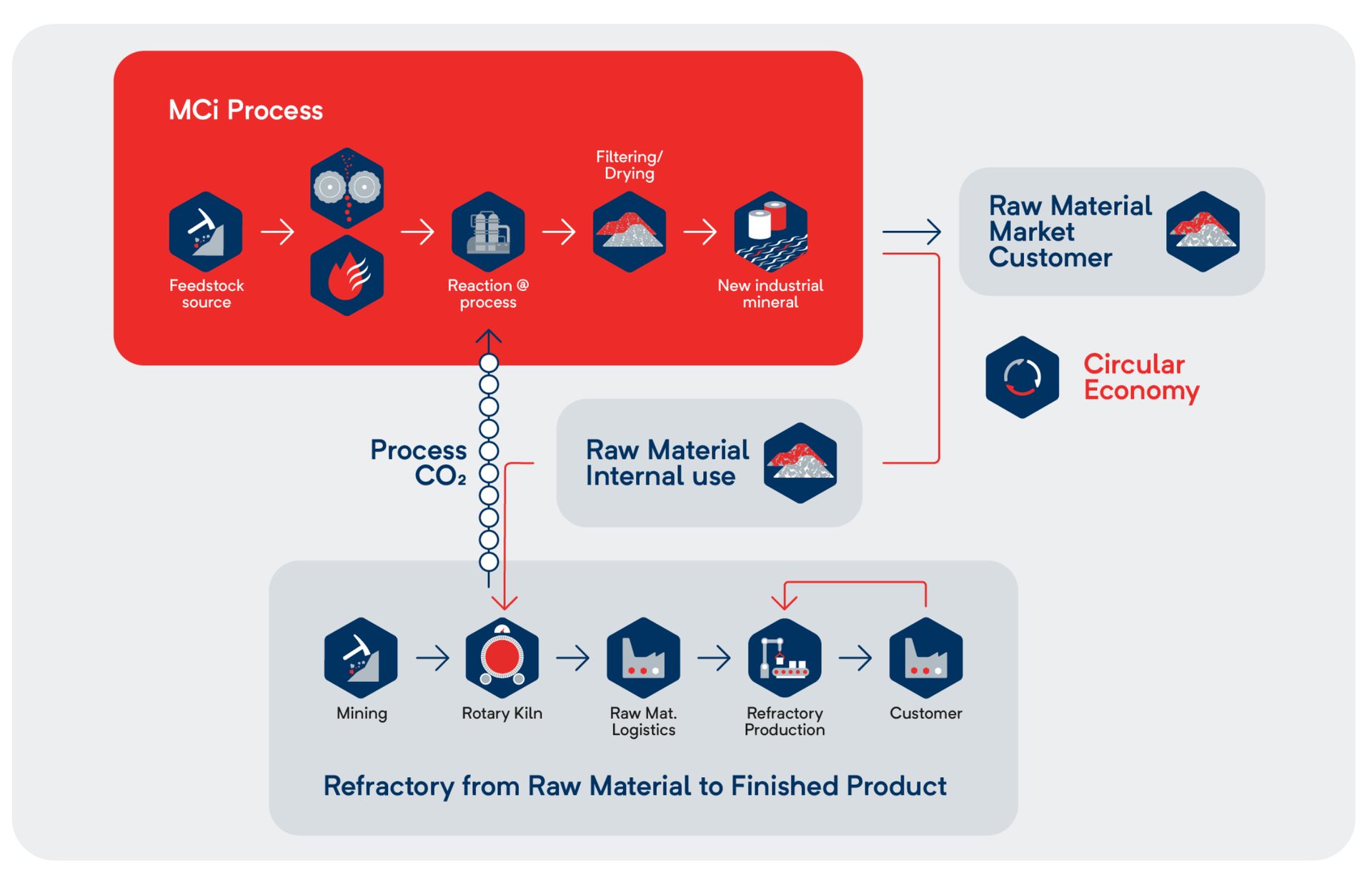
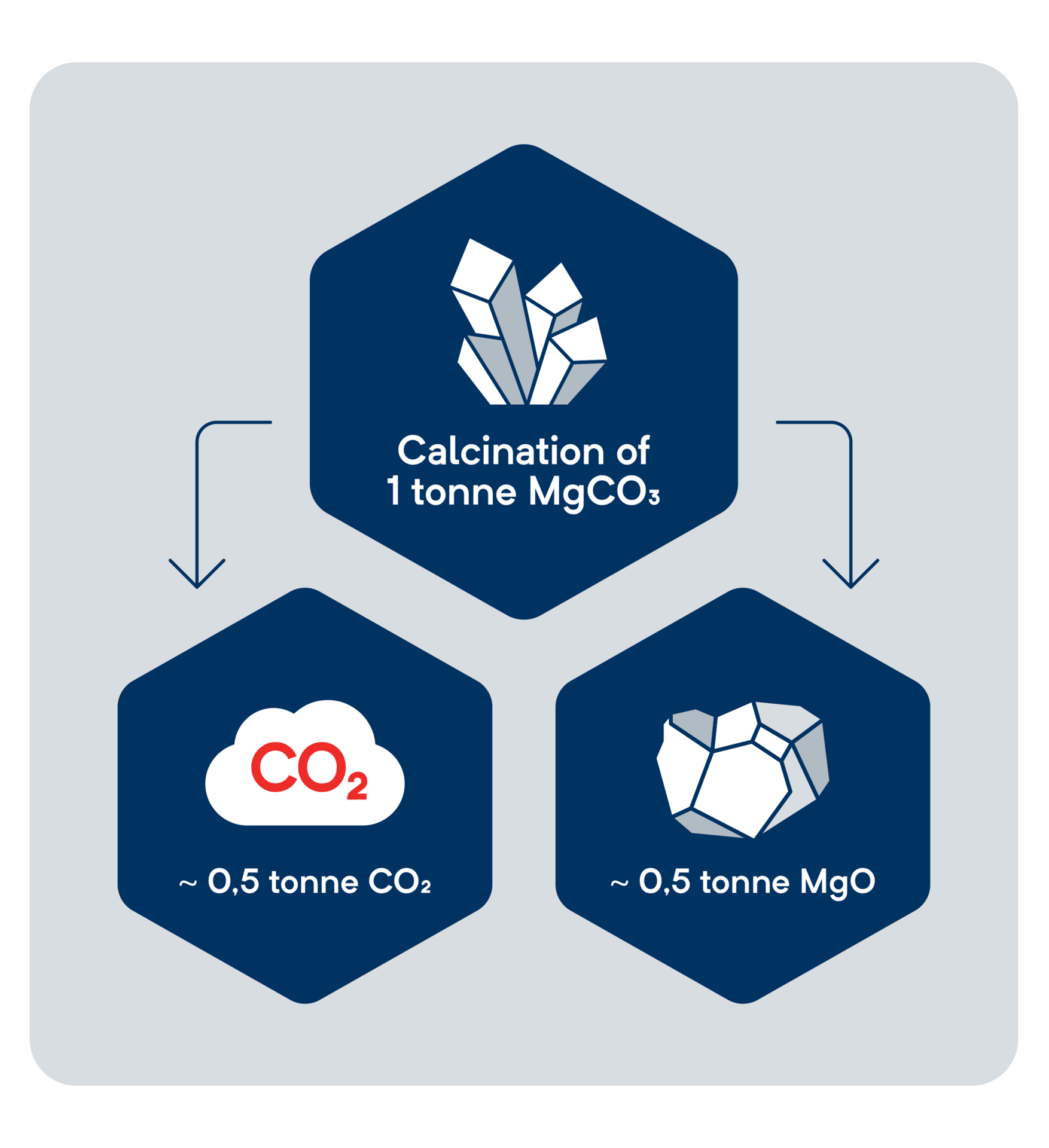
Mineralization of CO2 - MCi Carbon’s process
MCi Carbon has re-engineered the Earth’s natural process of storing CO2, known as mineral carbonation or weathering. This geological process, which typically takes millions of years, has been accelerated by MCi to just a matter of minutes in an industrial setting.
The technology combines captured CO2 with a mineral feedstock to produce valuable materials such as magnesium carbonate and amorphous silica. The raw materials are sourced from existing mining areas, while the end products are primarily delivered regionally, within a few hundred kilometers. RHI Magnesita will supply these low-carbon minerals to industries including cement, concrete, plasterboards, paper, and other applications.
These products are expected to be particularly attractive to the industrial minerals market—especially the cement industry, where they can significantly reduce the CO2 footprint of concrete. Over the long term, RHI Magnesita aims to contribute significant product volumes to substitute clinker on a large scale in the EU.
Additionally, magnesite will be processed using a CO₂-circular process and can then be used in the refractory industry—without additional CO₂ emissions from primary raw materials. This enables RHI Magnesita to make a meaningful contribution to decarbonization, both at the Hochfilzen site and across multiple industries
More about the process here: CO2 solution , MCi Materials
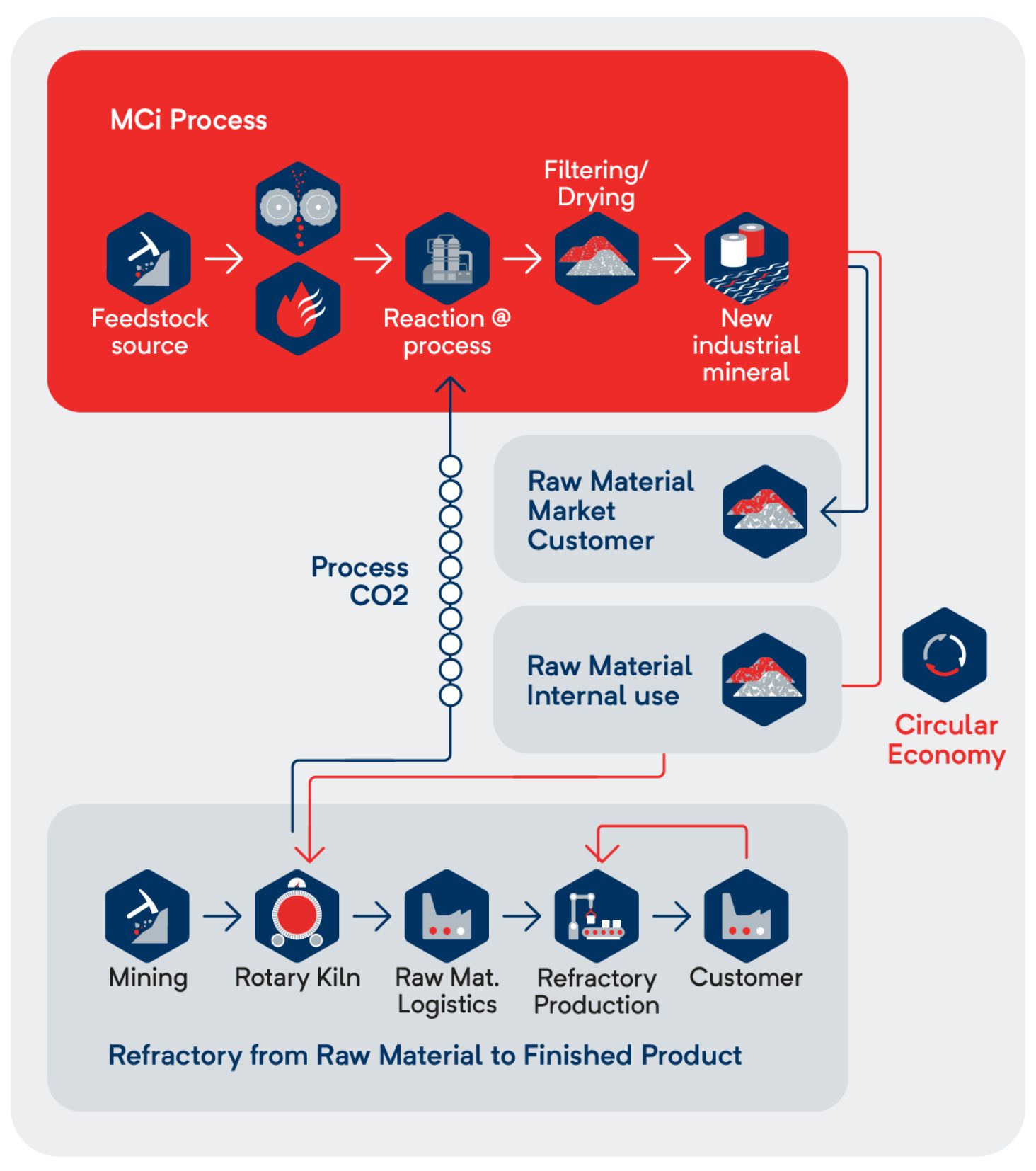
Mineralization of CO2 Process
Mineralization of CO2-
MCi Carbon’s process
Mineralization of CO2 Process
The technology combines captured CO2 with a mineral feedstock to produce valuable materials such as magnesium carbonate and amorphous silica. The raw materials are sourced from existing mining areas, while the end products are primarily delivered regionally, within a few hundred kilometers.
RHI Magnesita will supply these low-carbon minerals to industries including cement, concrete, plasterboards, paper, and other applications.
These products are expected to be particularly attractive to the industrial minerals market—especially the cement industry, where they can significantly reduce the CO2 footprint of concrete. Over the long term, RHI Magnesita aims to contribute significant product volumes to substitute clinker on a large scale in the EU.
Additionally, magnesite will be processed using a CO₂-circular process and can then be used in the refractory industry—without additional CO₂ emissions from primary raw materials. This enables RHI Magnesita to make a meaningful contribution to decarbonization, both at the Hochfilzen site and across multiple industries
More about the process here: CO2 solution , MCi Materials
MCi Carbon has re-engineered the Earth’s natural process of storing CO2, known as mineral carbonation or weathering.
This geological process, which typically takes millions of years, has been accelerated by MCi to just a matter of minutes in an industrial setting.
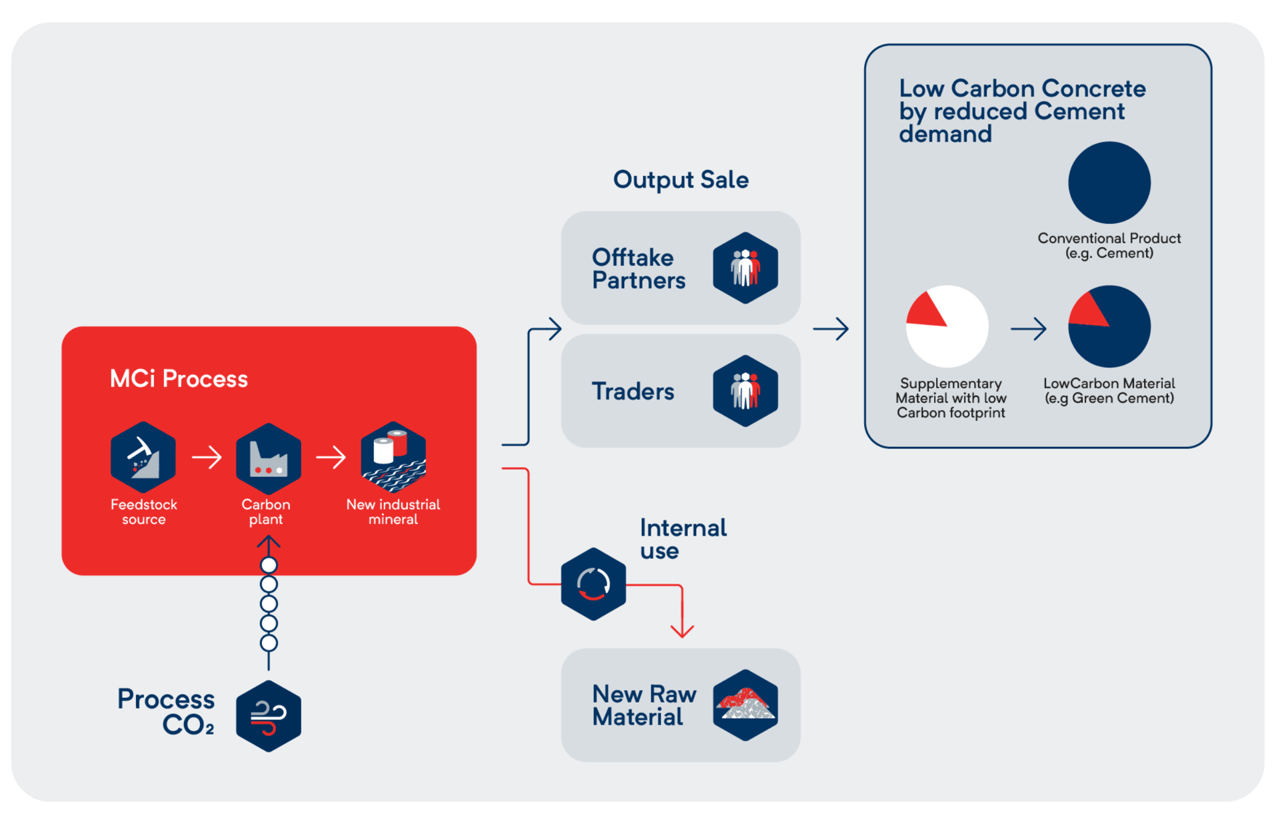
CCU Process Output
Magnesium carbonate
Amorphous silica
Low Carbon Materials
These minerals can be used in multiple applications, including:
Building materials (cement, concrete)
Refractory Ceramics
Plaster- and cardboards
Fertilizers
Paper production





CO2 Reduction in the Cement Industry
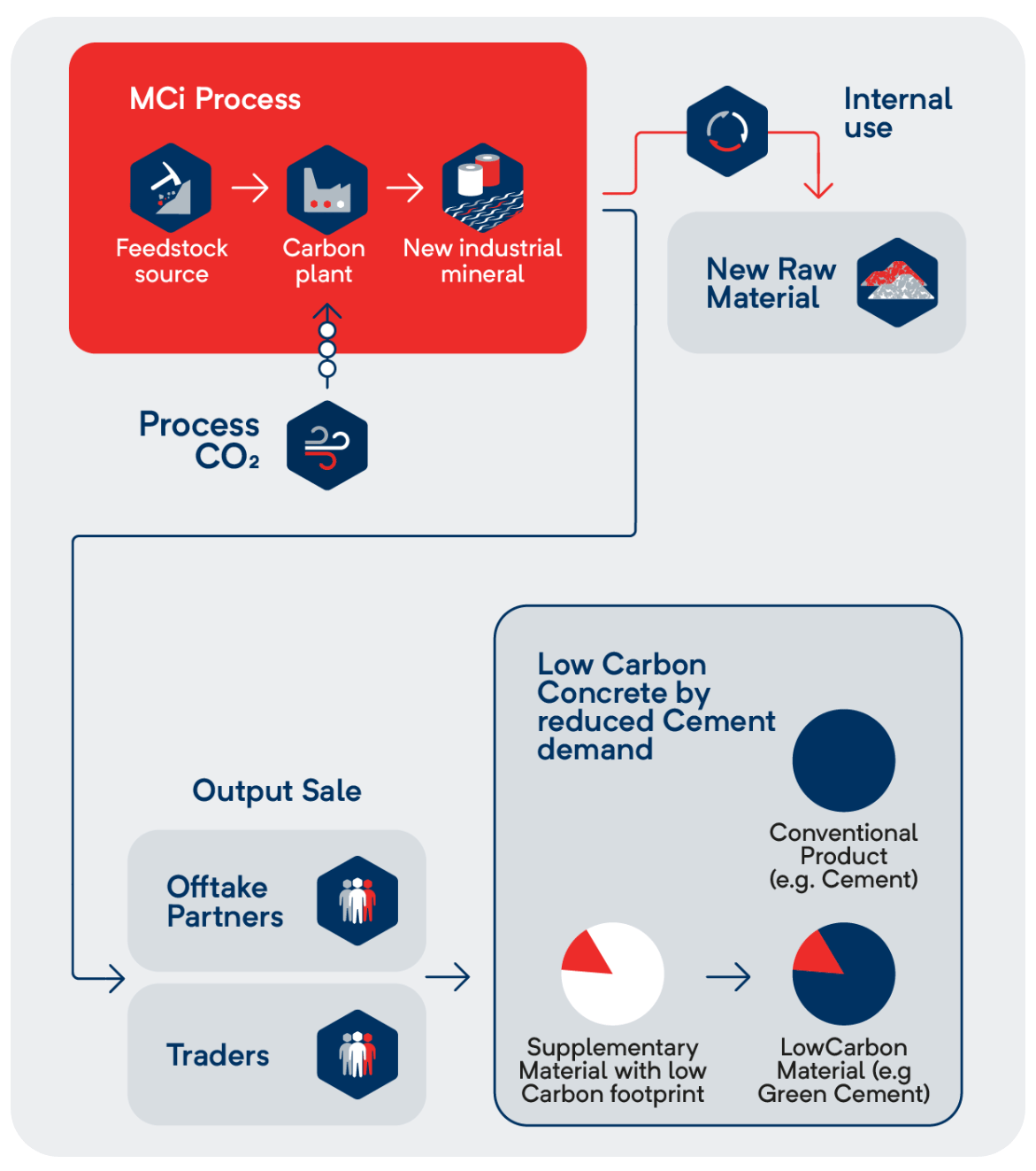
CCU Process Output
Magnesium carbonate
Amorphous silica
Low Carbon Materials
These minerals can be used in multiple applications, including:
Building materials (cement, concrete)
Refractory Ceramics
Plaster- and cardboards
Fertilizers
Paper production





CCU Process Output
Magnesium carbonate
Amorphous silica
Low Carbon Materials:
These minerals can be used in multiple applications, including:
Building materials (cement, concrete)
Refractory Ceramics
Plaster- and cardboards
Fertilizers
Paper production





CO2 Reduction in the Cement Industry
At our Hochfilzen site in Tyrol, Austria, RHI Magnesita plans to launch a first-of-its-kind commercial carbon capture and utilization (CCU) pilot plant by 2028, with a total investment of around €150 million. As part of the CCUpScale Project, between 50,000 and 100,000 tons of CO₂ will be captured annually from the exhaust stream and converted into chemically stable industrial minerals.
Project CCUpScale Pilotplant
Hochfilzen, Austria
In a second phase, targeted for the early 2030s, the Hochfilzen site is expected to achieve a 90% reduction in CO₂ emissions.
As one of the first commercial-scale CCU projects in the refractory industry, its financial viability will depend significantly on the availability of adequate public funding at both the national and EU levels. Looking ahead, the technology is intended to be scaled and implemented at other sites across Europe and globally. It also has the potential to serve as a decarbonization pathway for other hard-to-abate industries.
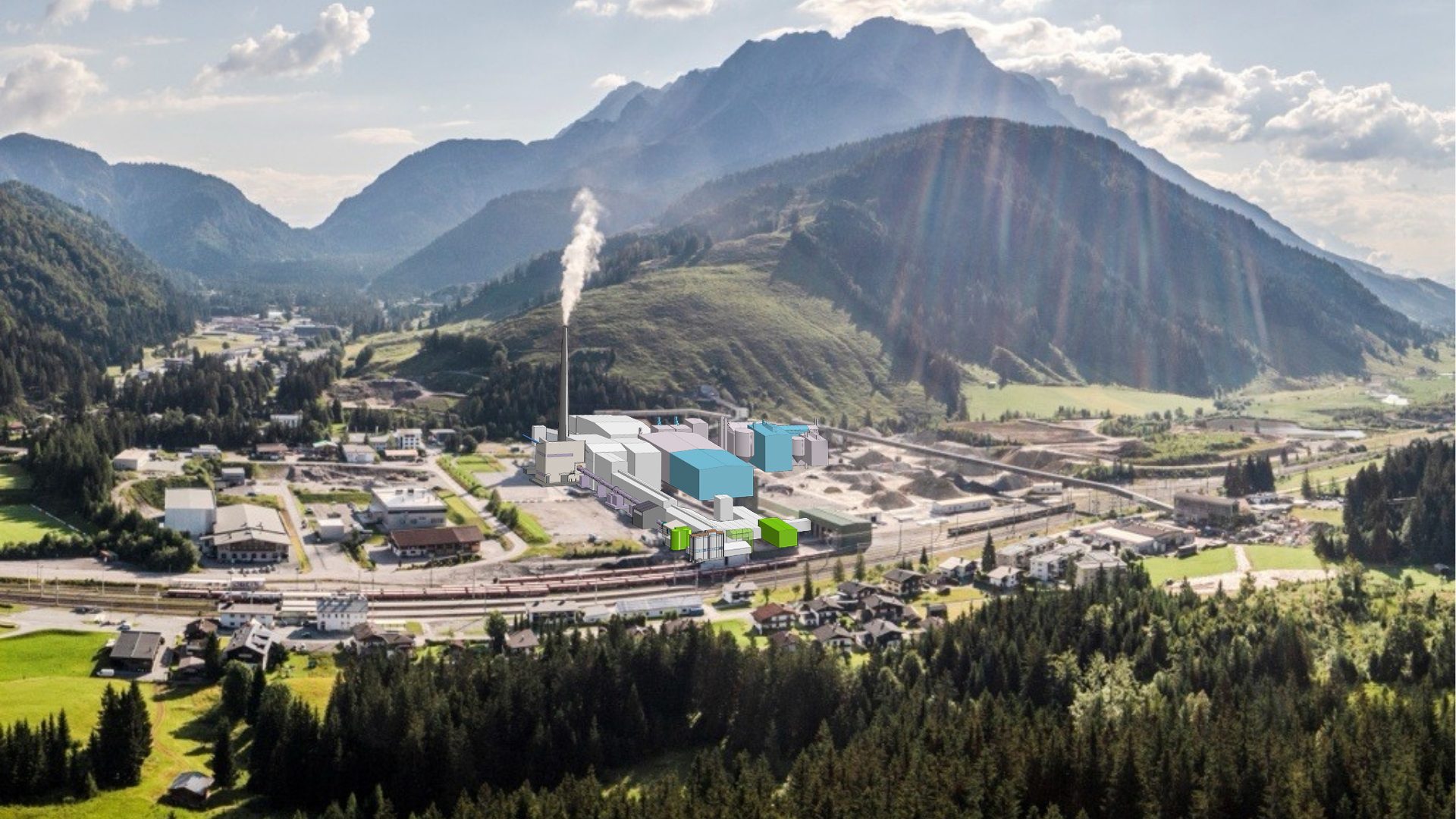


Project CCUpScale
Pilotplant
Hochfilzen, Austria
In a second phase, targeted for the early 2030s, the Hochfilzen site is expected to achieve a 90% reduction in CO₂ emissions.
As one of the first commercial-scale CCU projects in the refractory industry, its financial viability will depend significantly on the availability of adequate public funding at both the national and EU levels.
Looking ahead, the technology is intended to be scaled and implemented at other sites across Europe and globally. It also has the potential to serve as a decarbonization pathway for other hard-to-abate industries.
At our Hochfilzen site in Tyrol, Austria, RHI Magnesita plans to launch a first-of-its-kind commercial carbon capture and utilization (CCU) pilot plant by 2028, with a total investment of around €150 million. As part of the CCUpScale Project, between 50,000 and 100,000 tons of CO₂ will be captured annually from the exhaust stream and converted into chemically stable industrial minerals.


Realisation Year
Year
Projected CO2 Saved
by 2028
Tons
CCUpScale Project
Funding Received
Euros
Realisation Year
Year
Projected CO2 Saved
by 2028
Tons
CCUpScale Project
Funding Received
Euros
Realisation Year
Year
Projected CO2 Saved
by 2028
Tons
CCUpScale Project
Funding Received
Euros
Relevant Policies for CCU Development
Relevant Policies for CCU Development
Relevant Policies for CCU Development
Relevant Policies for CCU Development



European Forum Alpbach 2023 – Panel on Decarbonisation Technologies
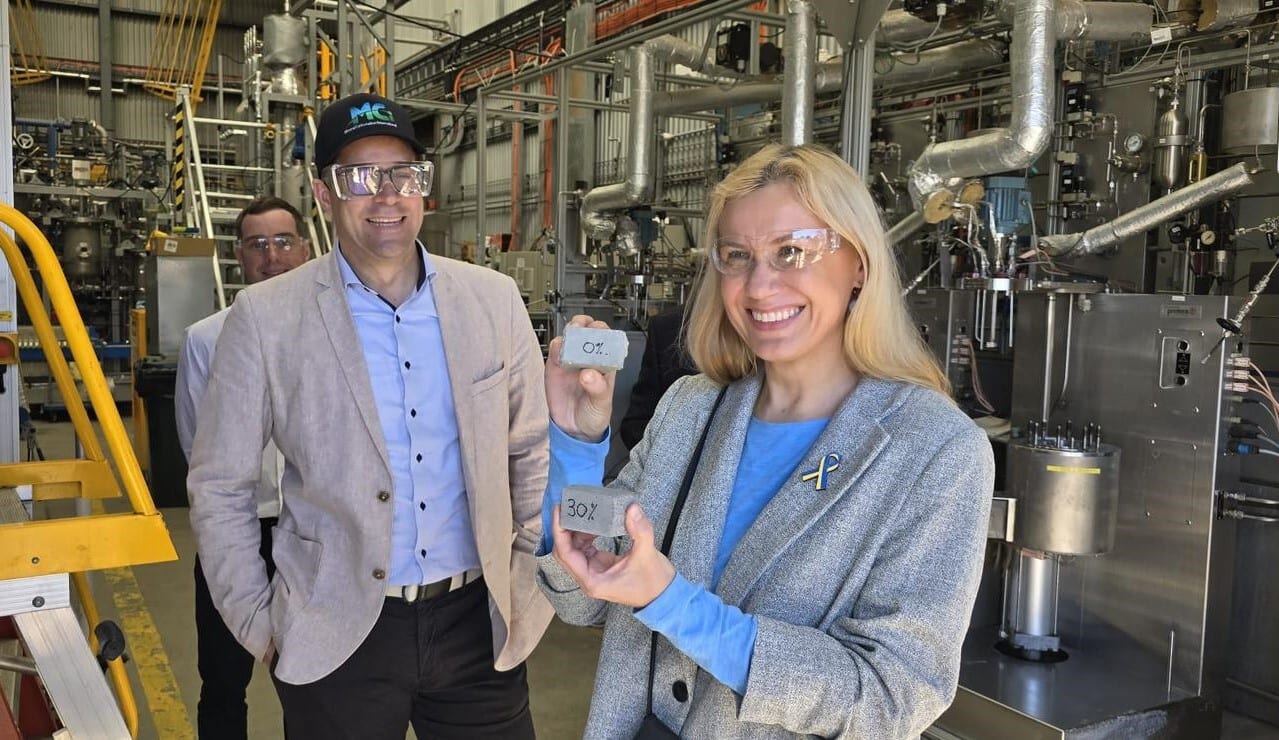

European Energy Commissioner, Kadri Simson, visits MCi Carbon in Australia

MCi Carbon lays Myrtle foundation for global industrial decarbonisation
CCU Innovation in Action

RHIM CCUpScale Project wins at COP29

The world's first CCU plant in the refractory industry

European Forum Alpbach 2023 – Panel on Decarbonisation Technologies

European Energy Commissioner, Kadri Simson, visits MCi Carbon in Australia

MCi Carbon lays Myrtle foundation for global industrial decarbonisation
CCU Innovation in Action

RHIM CCUpScale Project wins at COP29

The world's first CCU plant in the refractory industry
At the beginning of 2025, the CCUpScale project received over €3.8 million in initial funding through the Australia-Austria Industrial Decarbonisation Demonstration Partnership Program. This grant supports the collaboration between RHI Magnesita, MCi Carbon (MCi), the Austrian Institute of Technology (AIT), and the University of Technology Sydney (UTS) to advance industrial decarbonization.
The funding is provided by the Austrian Climate and Energy Fund, supported by the Austrian Ministry for Climate Action, the Austrian Research Promotion Agency (FFG), and the Australian Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment, and Water (DCCEEW).
International Recognition and Funding

This project aims to further develop MCi Carbon’s mineral carbonation technology and support RHI Magnesita’s plans to build the world’s first Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU) plant in the refractory industry in Hochfilzen, Austria.
Furthermore, the „CCUpScale“ project was honored at COP29, winning Most Outstanding Project – Austria in the Mission Innovation Net Zero Industries Awards. Co-chaired by Australia and Austria, the goal of the mission is to catalyse the development and demonstration of cost competitive solutions for the efficient decarbonisation of hard-to-abate energy intensive industries worldwide by 2030.



Furthermore, the „CCUpScale“ project was honored at COP29, winning Most Outstanding Project – Austria in the Mission Innovation Net Zero Industries Awards. Co-chaired by Australia and Austria, the goal of the mission is to catalyse the development and demonstration of cost competitive solutions for the efficient decarbonisation of hard-to-abate energy intensive industries worldwide by 2030.
This project aims to further develop MCi Carbon’s mineral carbonation technology and support RHI Magnesita’s plans to build the world’s first Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU) plant in the refractory industry in Hochfilzen, Austria.
The funding is provided by the Austrian Climate and Energy Fund, supported by the Austrian Ministry for Climate Action, the Austrian Research Promotion Agency (FFG), and the Australian Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment, and Water (DCCEEW).
At the beginning of 2025, the CCUpScale project received over €3.8 million in initial funding through the Australia-Austria Industrial Decarbonisation Demonstration Partnership Program. This grant supports the collaboration between RHI Magnesita, MCi Carbon (MCi), the Austrian Institute of Technology (AIT), and the University of Technology Sydney (UTS) to advance industrial decarbonization.
International Recognition and Funding


The funding is provided by the Austrian Climate and Energy Fund, supported by the Austrian Ministry for Climate Action, the Austrian Research Promotion Agency (FFG), and the Australian Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment, and Water (DCCEEW).
This project aims to further develop MCi Carbon’s mineral carbonation technology and support RHI Magnesita’s plans to build the world’s first Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU) plant in the refractory industry in Hochfilzen, Austria.
Furthermore, the „CCUpScale“ project was honored at COP29, winning Most Outstanding Project – Austria in the Mission Innovation Net Zero Industries Awards. Co-chaired by Australia and Austria, the goal of the mission is to catalyse the development and demonstration of cost competitive solutions for the efficient decarbonisation of hard-to-abate energy intensive industries worldwide by 2030.
At the beginning of 2025, the CCUpScale project received over €3.8 million in initial funding through the Australia-Austria Industrial Decarbonisation Demonstration Partnership Program. This grant supports the collaboration between RHI Magnesita, MCi Carbon (MCi), the Austrian Institute of Technology (AIT), and the University of Technology Sydney (UTS) to advance industrial decarbonization.
International Recognition and Funding
To the top ↑